MultiAgentBench : Evaluating the Collaboration and Competition of LLM agents
Jul 30, 2025·,,,,,,,,,,·
0 min read
Kunlun Zhu
Hongyi Du
Zhaochen Hong
Xiaocheng Yang
Shuyi Guo
Zhe Wang
Zhenhailong Wang
Cheng Qian
Robert Tang
Heng Ji
Jiaxuan You
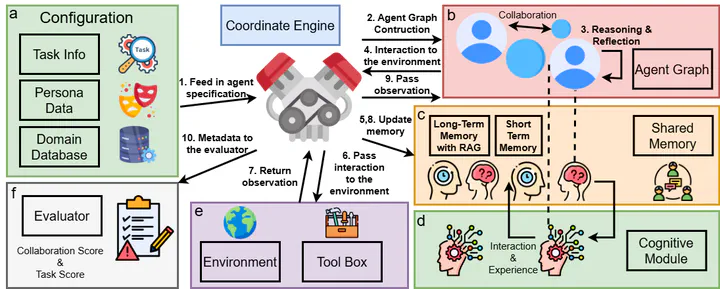 MARBLE: showcasing interactions between task information, persona data, domain databases, memory modules, and the environment through the coordinate engine and cognitive module.
MARBLE: showcasing interactions between task information, persona data, domain databases, memory modules, and the environment through the coordinate engine and cognitive module.Abstract
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities as autonomous agents; yet existing benchmarks either focus on single-agent tasks or are confined to narrow domains, failing to capture the dynamics of multi-agent coordination and competition. In this paper, we introduce MultiAgentBench, a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate LLM-based multi-agent systems across diverse, interactive scenarios. Our framework measures not only task completion but also the quality of collaboration and competition using novel, milestone-based key performance indicators. Moreover, we evaluate various coordination protocols (including star, chain, tree, and graph topologies) and innovative strategies such as group discussion and cognitive planning. Notably, cognitive planning improves milestone achievement rates by 3%. Code and dataset will be made publicly available. Code and datasets are publicavailable at https://github.com/ulab-uiuc/MARBLE
Type
Publication
Proceedings of the 63rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)